
Java has been around for decades, though it can still be considered young when compared to other languages. This makes Go an ideal choice for low-level programming projects and applications where performance is crucial. The difference here, however, is that Go lets programmers manually manage memory resources, giving you more control over memory usage. Go, meanwhile, also has a garbage collector. This leads to fewer memory leaks and segmentation faults. This feature makes it so that Java programmers do not need to manually manage memory, as the JVM handles the memory allocation and deallocation for you. Speaking of garbage collection, one primary benefit of Java is the fact that it has an automatic memory management and resource allocation utility in the form of its garbage collector. Read: Top Online Courses to Learn Java Memory Management However, Java does have built-in performance optimizations courtesy of the JVM and its garbage collection utilities that can make the performance of Java applications comparable to Go in most situations. Java’s concurrency is a bit bulkier than Go’s, which is more lightweight and can, in some instances, contribute to Go applications being a little more performant. Java also allows for concurrency through the Concurrency API, which lets developers take advantage of threads, locks, and synchronized blocks. Go uses Goroutines and channels to perform concurrent execution. Performanceįrom a performance perspective, Go supports concurrency and multi-threading, making it very efficient in terms of handling multiple processing tasks at the same time.
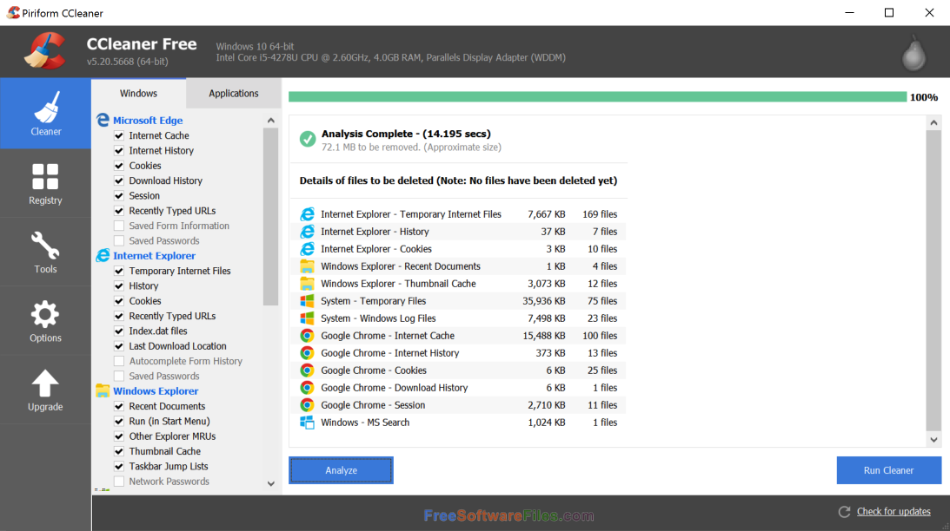
#FREE DOWNLOAD CCLEANER FOR WINDOW 7 CODE#
Golang code is more concise than Java and considered to be more human readable, making it a simpler language to learn, understand, maintain, and debug. It focuses on concepts such as explicit type declarations and composition versus the use of inheritance. Go, on the other hand, uses a more minimalistic approach to its syntax, favoring readability and maintainability. It makes uses of many Object-oriented principles, including classes, objects, polymorphism, encapsulation, inheritance, and interfaces. Programmers familiar with those languages will have a much easier time learning Java. Java, for its part, is similar to the C-family of languages, which include C, C#, and C++. There are several differences between Java and Go in terms of syntax. What are the Differences Between Java and Go?īelow we highlight some of the differences between Java and Go, including: If you are interested in learning more about Go, we have a great selection of Golang programming tutorials to get you started.
#FREE DOWNLOAD CCLEANER FOR WINDOW 7 SOFTWARE#
It is typically used for large-scale software projects, especially those that rely on concurrency and networking. Google designed the language with a mindset towards performance, security, and ease of use. Go – also known as Golang – is a programming language created by Google back in 2007, making it a relatively new language when compared to its contemporaries. We have a great section featuring hundreds of Java tutorials. It is known for its stability, wide-use, large library of extensions and frameworks, and community support. This means that programs created with Java can run on any platform that features the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), which encompasses most major systems. Java was created in the mid 1990’s with the philosophy of WORA, which stands for “write once, run anywhere”.
It is often attributed as being a full-fledged OOP language, but this is not quite true due to the fact that Java has both primitive and non-primitive data types. Java is a general purpose programming language with Object-oriented features. In particular, we will be comparing their syntax, performance, support, and features. In this tutorial, we will review each of these languages and examine how they differ from one another in an effort to help you choose the right option for your software project or career path. Two of those options include Java and Golang. Developers have a plethora of programming languages to choose from, each with its own unique set of features, strengths, and weaknesses.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
